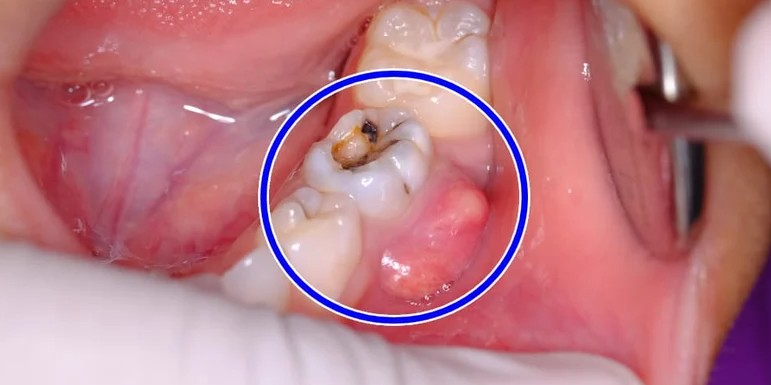
Tooth pain, swelling, or strange sensations in your mouth might not seem urgent at first. But sometimes, those symptoms signal something far more serious: an infected tooth. Left untreated, a tooth infection can spread beyond the gums, affecting your jaw, face, and even your overall health.
So, how can you tell if your tooth is infected? What signs should you look out for, and when is it time to get professional help?
At Asctorino, we believe early detection is the key to avoiding more invasive and costly procedures. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover the telltale signs of a tooth infection, why they happen, how they’re treated, and what steps you should take to protect your health if you notice symptoms.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, also called a dental abscess, occurs when bacteria enter the innermost part of the tooth—called the pulp—and begin to multiply. This usually happens because of untreated cavities, cracks, gum disease, or trauma.
As the infection grows, pus builds up in the tooth or surrounding tissues, leading to swelling, pain, and in severe cases, the spread of bacteria to other parts of the body.
There are three main types of dental abscesses:
Periapical abscess – Infection at the tip of the tooth’s root
Periodontal abscess – Infection in the gums around the tooth
Gingival abscess – Infection in the gum tissue, not affecting the tooth or bone directly
All three require treatment, but periapical and periodontal abscesses are especially serious if left untreated.
Early Warning Signs of a Tooth Infection
Recognizing the signs of a tooth infection early can help prevent complications and ensure faster healing. If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, your body might be trying to tell you that something’s wrong:
1. Persistent, Throbbing Tooth Pain
This is often the first and most common symptom. It may start mild and worsen over time, or come on suddenly. The pain may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck.
2. Sensitivity to Hot or Cold
A sharp or lingering sensitivity when eating hot soup or drinking cold beverages may be a red flag—especially if it’s isolated to one tooth.
3. Swollen Gums or Face
Infection causes inflammation. If one side of your face or gums appears swollen or puffy, and especially if the area is tender, an abscess could be forming.
4. Bad Taste or Odor in the Mouth
An unpleasant taste or smell may indicate that pus is draining from an infected tooth or gum pocket.
5. Fever and Fatigue
When the infection spreads, your immune system activates. A mild to high fever, chills, and a feeling of being run down are all signs that the infection may be systemic.
6. A Small Bump on the Gums
This pimple-like bump near a tooth is a fistula—a drainage point where pus escapes. While it may reduce pain temporarily, the infection still exists underneath.
7. Difficulty Chewing or Biting
An infected tooth can feel “high” or different from others. If chewing or applying pressure triggers intense pain, it’s time to see a dentist.
8. Jaw Stiffness or Difficulty Opening Your Mouth
This may indicate that the infection has begun to spread into deeper tissues around the tooth or into the jawbone itself.
At Asctorino, we urge you not to ignore these warning signs. Dental infections do not heal on their own and can become serious within days.
What Causes a Tooth Infection?
Tooth infections begin when bacteria breach the tooth’s protective layers.
Common causes include:
Untreated cavities – Bacteria erode enamel and dentin, reaching the pulp
Cracks or chips – These can expose the inner layers of a tooth to bacteria
Deep gum disease – Periodontal pockets harbor harmful microbes
Failed dental work – Old fillings or crowns that become loose may let bacteria in
Trauma – A blow to the tooth that damages the root or pulp
Even good oral hygiene can sometimes fall short if a cavity goes unnoticed. Regular dental exams help catch these problems early—before infection sets in.
What Happens If a Tooth Infection Is Left Untreated?
A dental infection may start small, but it can spread quickly if not treated. As the bacteria multiply, the infection can:
Destroy the surrounding bone and tissue
Spread into the jaw, cheeks, and neck
Reach the bloodstream, causing sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition
Lead to complications like sinus infections or brain abscesses in rare but severe cases
That’s why it’s critical not to “wait and see.” Pain may subside temporarily if the abscess drains, but the underlying infection remains and will likely return.
Diagnosis: How Dentists Confirm a Tooth Infection
When you visit a dentist with suspected tooth infection symptoms, they will:
Conduct a visual exam to check for swelling, drainage, or gum abscesses
Take X-rays to identify infections at the root or bone level
Test tooth sensitivity using temperature or percussion tests
Ask about your pain level, health history, and any recent dental work
Based on these findings, the dentist will confirm whether an infection is present and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Infected Teeth
Treating a tooth infection depends on its location, severity, and the condition of the tooth.
Common options include:
1. Root Canal Therapy
If the tooth’s pulp is infected but the structure is salvageable, a root canal removes the infected tissue and seals the tooth to prevent reinfection.
2. Tooth Extraction
If the tooth is severely damaged or cannot be saved, it may be removed entirely to eliminate the infection source.
3. Incision and Drainage
For large abscesses, the dentist may create a small incision in the gum to allow the pus to drain, relieving pressure and pain.
4. Antibiotics
Dentists often prescribe antibiotics to stop the spread of infection. However, antibiotics alone won’t cure the problem—they’re typically used in combination with a procedure to remove the infected tissue.
5. Pain Management
Over-the-counter or prescription medications can be used to relieve discomfort while treatment is ongoing.
Asctorino always recommends addressing the root cause—not just the symptoms—to prevent further complications.
Home Remedies: Can You Treat a Tooth Infection Yourself?
You may find temporary relief at home using:
Saltwater rinses to clean the mouth and reduce swelling
Cold compresses to numb the pain and control facial swelling
Clove oil or OTC gels to temporarily numb the affected area
Ibuprofen or acetaminophen to reduce inflammation and discomfort
But be aware: these are not cures. Home remedies may help you cope while waiting for treatment, but they won’t eliminate the infection.
When to Seek Emergency Dental Care
Some infections require immediate medical attention, especially if symptoms escalate.
Go to an emergency dentist or hospital right away if you have:
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
Swelling in the neck, under the jaw, or around the eye
Fever that won’t subside
Rapid heartbeat or confusion
Uncontrolled bleeding in the mouth
Persistent pain despite taking medication
An infection that spreads to vital areas of the body can be life-threatening, so don’t hesitate to seek urgent help.
Preventing Tooth Infections
Good oral hygiene and routine dental visits are your best defense.
Here’s how to reduce your risk:
Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
Floss daily to remove plaque and food debris
Avoid sugary foods and drinks that fuel bacteria
Get cavities filled early before they reach the pulp
Replace old fillings or crowns before they become loose
Schedule dental exams and cleanings every six months
At Asctorino, we focus on proactive dental care to keep minor issues from becoming serious infections.
FAQs
1. How do I know if my tooth pain is from an infection?
If the pain is severe, throbbing, or accompanied by swelling, bad taste, or fever, it may be caused by an infection. A dental X-ray is the best way to confirm the diagnosis.
2. Can a tooth infection go away on its own?
No. Even if symptoms temporarily improve, the infection will persist and may worsen. Only professional treatment can fully eliminate it.
3. How long can a tooth infection go untreated?
You may have a few days to a couple of weeks before complications arise, but once the infection spreads, it can become a serious medical emergency. Don’t delay treatment.
4. Can I treat a tooth infection without antibiotics?
In some cases, such as after a root canal or extraction, antibiotics may not be needed. But when infection is spreading or systemic, antibiotics are often essential.
5. Is a gum bump always a sign of infection?
Not always. Gum bumps can be caused by cysts, trauma, or irritation. However, if pus or pain is present, it may indicate an abscess and should be evaluated by a dentist.
Final Thoughts
Recognizing the early signs of a tooth infection can prevent serious health complications—and spare you from unnecessary pain and expense. If you notice persistent pain, swelling, or fever, don’t wait to take action.
At Asctorino, we’re here to guide you every step of the way, from diagnosis to treatment and prevention. Whether you’re experiencing discomfort now or want to safeguard your future oral health, trust us to help you protect your smile—and your well-being.